* Heat type
Formulas :

with the following provisions:
Q = Heat received a substance (Joule, kilojoules, calories, kilocalories)
M = Mass of substance (Gram, Kilogram)
C = Heat type (Joule / kilogram ° C, Joule / gram ° C, Calories / gram ° C)
 = Changes in temperature (° C) → (t2 - t1)
= Changes in temperature (° C) → (t2 - t1)
M = Mass of substance (Gram, Kilogram)
C = Heat type (Joule / kilogram ° C, Joule / gram ° C, Calories / gram ° C)
 = Changes in temperature (° C) → (t2 - t1)
= Changes in temperature (° C) → (t2 - t1) * To find the heat type, the formula is:
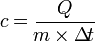
* To find the mass of substance, the formula is:

* Heat Capacity
Heat capacity is the amount of heat needed by the body to raise its temperature 1 ° C.
* The formula for heat capacity:
rovided that:
Q = Heat received a substance (Joule, kilojoules, calories, kilocalories)
H = Heat capacity (Joules / ° C)
M = Mass of substance (Gram, Kilogram)
C = Heat type (Joule / kilogram ° C, Joule / gram ° C, Calories / gram ° C)
 = Changes in temperature (° C) → (t2 - t1)
= Changes in temperature (° C) → (t2 - t1)
Q = Heat received a substance (Joule, kilojoules, calories, kilocalories)
H = Heat capacity (Joules / ° C)
M = Mass of substance (Gram, Kilogram)
C = Heat type (Joule / kilogram ° C, Joule / gram ° C, Calories / gram ° C)
 = Changes in temperature (° C) → (t2 - t1)
= Changes in temperature (° C) → (t2 - t1) 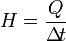
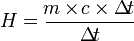

Formulas:

with the following provisions:
Q = Heat received a substance (Joule, kilojoules, calories, kilocalories)
M = Mass of substance (Gram, Kilogram)
L = Heat melting substances (Joule / kg, kilojoules / kilogram, joule / gram)
Q = Heat received a substance (Joule, kilojoules, calories, kilocalories)
M = Mass of substance (Gram, Kilogram)
L = Heat melting substances (Joule / kg, kilojoules / kilogram, joule / gram)
* Steam Heat
Formulas:
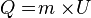
with the following provisions:
Q = Heat received a substance (Joule, kilojoules, calories, kilocalories)
M = Mass of substance (Gram, Kilogram)
U = Heat steam substances (Joule / kg, kilojoules / kilogram, joule / gram)
Q = Heat received a substance (Joule, kilojoules, calories, kilocalories)
M = Mass of substance (Gram, Kilogram)
U = Heat steam substances (Joule / kg, kilojoules / kilogram, joule / gram)
* Principle Black Formulas:
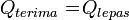
The principle of Black: The amount of heat received equal to the amount of heat released *Example Problem:
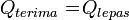
The principle of Black: The amount of heat received equal to the amount of heat released *Example Problem:
1.How much heat energy needed to vaporize 5 Kg of water at its boiling point, if the steam heat 2.26 million Joules / Kilogram? Answer: Given: m = 5 kg
U = 2,260,000 J / Kg Asked: Q =..... ? Answer Q = m x U
= 5 kg x 2.26 million J / Kg
= 11,300,000 J = 11.3 x 106 J
U = 2,260,000 J / Kg Asked: Q =..... ? Answer Q = m x U
= 5 kg x 2.26 million J / Kg
= 11,300,000 J = 11.3 x 106 J


Tidak ada komentar:
Posting Komentar